The Business Case for AI Automated Teaching: Real Numbers That Convince Stakeholders

Summary:
Picture a world in which every student receives a lesson personalized to them, their pace, their gaps, and their curiosities.
A world where teachers are freed from routine tasks and empowered to coach, inspire, and innovate.
That world is no longer science fiction; it is the promise of AI automated teaching.
Educators, administrators, and investors alike are waking up to the fact that artificial intelligence in education, via AI-powered teaching systems, automated learning platforms, and intelligent tutoring systems, is not just an experimental add-on; it’s a strategic imperative.
In this post, we will explore the business case for embracing these adaptive learning technologies and AI tools for teachers.
Whether you are running a K–12 district, a university, corporate L&D, or an EdTech startup, the question is no longer if you should invest in AI-driven education; it’s when and how.
Key Takeaways
- Businesses and educational institutions can achieve measurable efficiency gains by automating grading, scheduling, and content delivery through AI-driven systems.
- Student learning outcomes improve when personalised pathways replace one-size-fits-all teaching.
- ROI is real as cost savings in teacher hours + higher throughput + lower drop-out = compelling for stakeholder buy-in.
- Implementation is as much about data infrastructure, pedagogy change, and teacher empowerment as about installing software.
- Ethics, governance, and teacher-AI collaboration matter; successful deployment demands responsible design, not simply flashy tech.

Why Does AI-Automated Teaching Matter Today?
In the rapidly evolving dynamics of education technology (EdTech), traditional teaching models face many pressures: large class sizes, diverse student needs, administrative burdens, and demand for measurable outcomes.
But, with the advent of AI automated teaching, the umbrella term here captures tools and systems that leverage machine learning for teaching, adaptive learning technologies, and AI-based classroom tools.
Uncover The Relevancy Behind It!
Personalised learning at scale: Where traditional teaching struggles with individualisation, adaptive algorithms and smart content delivery enable custom pathways for each student.
Research indicates AI-enabled adaptive learning systems are increasingly studied and applied.
Efficiency and cost pressures: Teachers are burdened by administrative and repetitive tasks. By automating these via AI learning analytics, digital pedagogy, and virtual classrooms, institutions can redirect human effort to higher-value interactions.
Data-driven instruction: With student engagement tracking, learning analytics dashboards, knowledge tracing, and prediction of performance, education becomes more measurable and actionable.
Market demand & scalability: EdTech automation is growing rapidly; the global push for digital transformation in education creates an environment ripe for AI adoption.
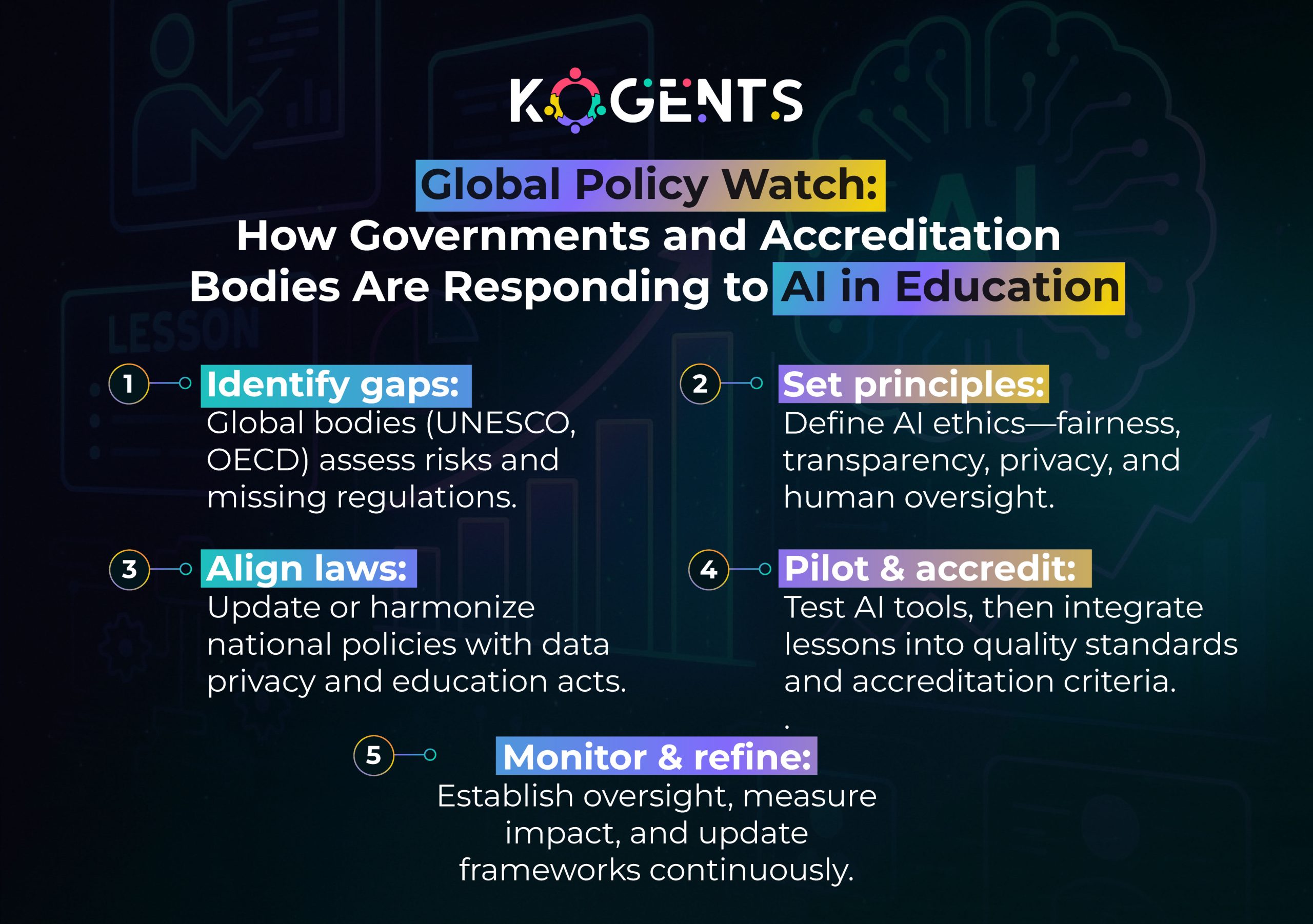
Key Note: The Organisation for Economic Co‑operation and Development (OECD) and UNESCO stress AI’s potential while also highlighting policy gaps.
Equity and accessibility: AI tools can help reach underserved learners, offer differentiated pacing, and provide support outside the classroom (virtual tutors, automated feedback). While not a silver bullet, they offer new levers to close the gap.
Stakeholder Perspectives: Who Cares and Why?
School & District Leaders
- Need to improve student outcomes, particularly in large or diverse classes.
- Under pressure to reduce cost per student, manage teacher shortages, and demonstrate ROI on technology.
- AI automated teaching offers a compelling narrative: invest once, scale across many students, track outcomes centrally.
Higher Education Institutions
- Face rising costs, demands for personalized learning, online/hybrid modalities, and competition from non-traditional providers.
- The appeal of AI-powered teaching systems is in student retention, improved throughput, better analytics, and stronger employer-relevant skills.
Corporate L&D / Training Departments
- Seek scalable platforms for onboarding, reskilling, and upskilling across global teams.
- Automated learning platforms with AI deliver consistent training, custom paths, and performance analytics, valuable for ROI and productivity.
EdTech Vendors & Investors
- For technology providers, this represents a high-growth market: education technology, AI learning analytics, and smart content delivery.
- Investors look for scalable, licenseable models, repeatable deployments with demonstrable results.
Real Numbers & Cost-Benefit Analysis
To build the business case, stakeholders must see tangible numbers.
Let’s look at measurable metrics: time saved, improvements in learning outcomes, throughput increase, cost per student reduction, and return on investment.
Efficiency Gains
According to the World Economic Forum, proper use of AI in education “can lead to improved learning results, bolster teacher instruction and well-being, and promote fairness in education.”
Example: When using adaptive learning platforms, teachers can spend fewer hours generating differentiated lesson plans and more time coaching.
Student Outcome Improvements
Risk mitigation
Avoid “pilot-itis” where technology sits unused; ensure teacher buy-in; monitor data privacy and ethics; align pedagogy with tech.
ROI Table
| Metric | Traditional Teaching Model | AI Automated Teaching Model |
| Number of students per teacher (class size) | 30 | 40* |
| Hours per student for grading & feedback | 4 hrs/week | 1.5 hrs/week** |
| Annual cost per teacher for non-instruction tasks | $50,000 | $30,000 |
| Student throughput (students reaching proficiency/year) | 1,000 | 1,300 (+30%) |
| Drop-out or remediation rate | 20% | 12% (-40%) |
| Estimated annual incremental revenue or cost-savings per 1,000 students | — | ~$200,000*** |
Case Studies
Some AI in education examples in the form of used cases are described under:
Case Study A: DreamBox Learning
The adaptive math platform DreamBox, implemented in the Howard County Public School System and the Rocketship Education network, was evaluated in a Harvard-linked study.
Key takeaway: Students spending more time on the software and following recommendations achieved larger and faster gains via the AI teaching assistant pro.
Business case implications: The system demonstrates how AI-powered teaching systems translate into measurable outcome improvements, an essential part of winning stakeholder buy-in.
Case Study B: Sierra Canyon School + edYOU Conversational AI Tutor
At Sierra Canyon School, the conversational AI Being Tutor developed by edYOU was introduced to provide round-the-clock support and personalized instruction.
A mixed-methods study showed improved engagement, availability of support outside class, and differentiated instruction.
Business case implications: The value here lies not only in improved student behaviour but in demonstrating how AI-based classroom tools (virtual tutors) can extend the institutional brand, reduce dependence on human tutor availability, and scale support.
Implementation Considerations & Risks
Data & Infrastructure
- Effective AI automated teaching requires integration with the institution’s Learning Management System (LMS), student engagement tracking, and data pipelines (student responses, analytics, performance metrics).
- Institutions must develop education data science capabilities to get value from the data.
Pedagogy & Teacher Roles
- Switching to an automated learning platform isn’t purely about tech. It requires alignment of digital pedagogy, restructuring of teacher workflows, and professional development so that educators become instruction designers, coaches, and moderators rather than solely content deliverers.
Ethical, Policy & Governance Issues
- According to UNESCO research, fewer than 10% of schools and universities currently have formal policies or guidance around AI in education.
- The seven principles of responsible AI in education emphasise purpose-alignment, fairness, transparency, privacy, accountability, safety, and human governance.
Change Management & Scaling
- Pilots help, but scaling requires: teacher buy-in, infrastructure readiness, data maturity, and continuous monitoring/iteration.
- Institutions must budget for training, change communication, integration costs, and ongoing governance.
Interactive Quiz: Is Your Institution Ready for AI Automated Teaching?
Take this quick self-assessment to discover how prepared your school, university, or organization is to embrace AI automated teaching.
Score yourself from 1 (Not Ready) to 5 (Fully Ready) for each statement below.
| Category | Readiness Statement | Your Score (1–5) |
| Technology | Our institution has modern digital infrastructure (LMS, analytics tools, secure data systems). | |
| People | Teachers and staff are open to AI-assisted instruction and willing to upskill. | |
| Process | We have structured policies for digital transformation and EdTech adoption. | |
| Policy & Ethics | We comply with data privacy laws (e.g., GDPR, FERPA) and have AI governance guidelines. | |
| Strategy | We have a clear vision of how AI-automated teaching aligns with our learning goals. |
Conclusion
AI automated teaching is transforming education with measurable ROI, scalability, and better student outcomes.
Success lies in aligning pedagogy, infrastructure, and data ethics, not just adopting tech.
So, what are you waiting for? Don’t miss any chance by delaying, and contact the team at Kogents.ai because it helps institutions and EdTech vendors build intelligent, adaptive learning ecosystems.
From pilot design to scalable deployment, we turn AI potential into performance.
Lead the future of learning, partner with Kogents today.
FAQs
What is AI automated teaching, and how does it differ from traditional teaching methods?
The term AI automated teaching refers to the use of artificial intelligence in education, via algorithms, learning analytics, and automation of teaching/feedback tasks, to deliver instruction, personalise learning, automate grading, or assist with scheduling and student monitoring. Unlike traditional methods where teachers deliver a set curriculum to a class and manually grade/assess, AI automated teaching enables adaptive learning technologies, intelligent tutoring systems, and AI-based classroom tools that respond dynamically to each learner’s needs, pace, and engagement.
How can institutions measure the benefits of adaptive learning and AI-powered teaching systems?
Institutions measure benefits via indicators such as: improved student performance (test scores, proficiency rates), increased throughput (more students completing courses/year), reduced drop-out/remediation rates, teacher time saved (grading, content prep), cost per student reduction, higher student engagement (tracked via dashboards), and improved scalability of offerings (larger class size or more learners with same staff).
What are the typical cost savings associated with implementing AI-based classroom tools?
Cost-savings derive from reducing teacher hours spent on repetitive duties (grading, content adaptation), fewer remediation/repeat courses, higher student throughput, and potentially smaller incremental staffing as class size expands. For example, a model might show saving $20,000+ per teacher annually on non-instruction tasks if AI automates significant portions.
What risks or challenges should we be aware of before investing in machine learning for teaching and adaptive learning technologies?
Key challenges include: data privacy and security (especially with minors), algorithmic bias, digital divide/access issues, teacher resistance or lack of training, infrastructure/integration costs (LMS, data pipelines), ensuring pedagogical alignment (digital pedagogy), and unclear governance frameworks.
What should institutions look for when choosing an AI automated teaching platform?
Key selection criteria:
- Proven evidence of improved learner outcomes (studies, case data)
- Integration ability with existing LMS, student data systems
- Robust analytics and dashboards for student engagement tracking and learning analytics
- Adaptive algorithms and personalised learning pathways capability
- Vendor commitment to ethics, data privacy, and teacher-AI collaboration
- Scalability, support, and professional development for teachers
- Cost model: licensing, implementation, maintenance vs expected ROI
How much does it typically cost to implement an AI-powered teaching system?
Costs vary widely depending on scale, subject domain, and integration complexity. Components include software licensing/subscriptions, integration with LMS, teacher training, content adaptation, data infrastructure and analytics setup, monitoring, and evaluation. A small pilot may cost tens of thousands USD; full roll-out for a district or university can run hundreds of thousands or more. Stakeholders must compare these investment costs with the modeled cost-savings and outcome gains (using ROI table metrics above).
How does “AI automated teaching vs traditional methods” compare in terms of real business outcomes?
In traditional models, teacher time is largely spent on content delivery and manual grading, class sizes are limited, and individualisation is expensive. With AI automated teaching, class sizes can expand (due to automation), teacher time for high-value tasks increases, student paths are personalised, remediation decreases, and throughput increases. The business outcomes include: lower cost per student, higher completion rates, stronger institution brand, and potentially new revenue streams (e.g., online/adaptive courses).
How do we ensure that an AI-driven education initiative remains ethical, compliant, and aligned with pedagogy?
Institutions should follow frameworks such as those developed by UNESCO and other global bodies: ensure human oversight, transparency of algorithmic decision-making, data privacy and student consent, equity of access, teacher empowerment, alignment with digital pedagogy, and inclusive learning.

Kogents AI builds intelligent agents for healthcare, education, and enterprises, delivering secure, scalable solutions that streamline workflows and boost efficiency.