AI in Education Examples That Transformed Ordinary Institutions into Global Leaders

Summary:
Imagine a classroom where each student receives real-time, personalised guidance, an intelligent system that adapts lessons to their pace, monitors engagement, flags when they’re about to disengage, and supports their teacher by automating routine tasks.
That is no longer science fiction; it is the world of Artificial Intelligence in Education, and it is transforming institutions from ordinary to extraordinary.
In this blog post, we dive into AI in education examples that have tipped the scales for schools, colleges, and online platforms, turning local classrooms into global leaders in teaching and learning.
Whether you are an educator, administrator, edtech founder, or policymaker, the story is clear: those who harness Machine Learning in Education, Intelligent Tutoring Systems, and Educational AI Tools are the ones setting the pace.
Key Takeaways
- Transformation is measurable as institutions leveraging AI in education report clear gains in outcomes, efficiency, and engagement.
- Personalisation at scale is no longer a dream; AI-powered tools for education are enabling tailored pathways for every learner.
- Teacher empowerment, not replacement, but the best uses of AI in schools offload routine tasks and let educators focus on higher-order teaching.
- Ethics, policy, and data privacy matter when scaling AI in education, bringing governance, bias mitigation, and responsible AI to the fore.
- Global leadership emerges when institutions adopt AI early, iterate thoughtfully, and measure impact, turning ordinary into extraordinary.
What is “AI in Education: Examples”?
When we talk about AI in education examples, we refer to concrete, operational deployments of artificial intelligence technologies within the teaching-learning ecosystem.
These Examples of AI in Education can include:
- An AI Tutoring for students that personalizes exercises to each student’s knowledge gaps.
- Analytics dashboards using learning analytics to monitor engagement, performance, and predict dropout.
- Administrative systems using data-driven instruction and curriculum automation to optimise scheduling and resource allocation.
- Online platforms deliver adaptive learning modules, using machine-learning models to adjust content on the fly.
Why institutions adopt AI: Use of AI in Schools & Higher Education?
Institutions are under pressure: rising costs, diverse learner profiles, remote and hybrid demand, teacher shortages, and the imperative to deliver personalised learning at scale.
The AI agents for higher education addresses these pressures by:
- Curbing teacher workload: automating grading, feedback, and routine content creation.
- Enhancing student engagement: interactive, intelligent content, avatars, chatbots, personalised paths.
- Better outcomes: Several studies show improved test scores when AI-adaptive systems are used.
- Scaling access: for remote learners, underserved groups, and special-needs students, AI offers inclusive solutions.
Key Enabling Technologies & Topical Clusters
Adaptive Learning, Learning Analytics, Personalized Learning
- Adaptive learning systems monitor a student’s responses and dynamically adjust content, difficulty, pacing, and remediation paths. This means each learner follows a path unique to them, promoting mastery rather than uniform instruction.
- Learning analytics refers to the collection and analysis of data from student interactions with digital tools: time-on-task, answer patterns, engagement metrics, and drop-off points.
- Personalized learning refers to the broader pedagogical goal enabled by AI that offers individualized learning paths that suit each learner’s strengths, weaknesses, pace, interests, and needs.
Edtech, Smart Classrooms, Student Engagement
- Schools are becoming smart classrooms: connected devices, IoT sensors, AI-driven interactions, digital assistants. These settings promote student engagement, as learning becomes interactive, responsive, and less passive.
- Education technology (edtech) is the umbrella term under which AI tools sit: LMS (learning management systems), VLE (virtual learning environments), digital assessments, and content platforms.
AI-powered Tutoring, Curriculum Automation, Data-Driven Instruction
- AI-powered tutoring means virtual chatbots that mimic aspects of human tutoring: giving prompts, guiding thinking, and asking scaffolding questions.
- Curriculum automation refers to the use of AI to assist in planning, sequencing of lessons, content generation, and aligning assessments, freeing teachers to focus on pedagogy rather than administrative design.
- Data-driven instruction is the practice of using real-time analytics and AI-insights to guide instructional decisions: who needs remediation? Which topic is fuzzy for a class cohort? Where to focus teacher time?
Case Studies: Transformational Examples
Here we present three concrete case studies, institutions that adopted AI and transformed from ordinary to globally competitive.
Case Study A – K-12 School District
Bolton College (UK) from one case-list: In one documented case study, it faced challenges creating engaging online learning videos.
- They used an AI-powered video creation platform (via Synthesia) to automate video generation.
- Teachers input scripts, chose an AI avatar, and the system created ready-to-use videos.
Outcome: This enabled increased output and better scalability.
Transformative Insight:
- By replacing manual video creation with AI automation, the school boosted content production capacity.
- Educators regained time to focus on teaching and engagement.
- The quality and scalability of lessons improved dramatically.
- Even modest institutions can leverage educational AI tools to become digital-learning leaders.
Case Study B – University & Intelligent Tutoring / Analytics
Loyola University Chicago implemented an AI-powered digital assistant (“LUie”) built on the Oracle Digital Assistant platform to support student queries around the clock.
The assistant integrated with administrative systems and provided real-time answers to common student questions.
Early results: accuracy improved from ~86% to ~91%, and student satisfaction was ~91% positive.
Case Study C – Online Learning Platform / Adaptive Learning
Transformative Insight: By using machine learning for adaptive education, institutions can scale personalised, high-quality learning globally and achieve measurable outcome gains.
Table: Comparison of Institutions, AI Applications & Outcomes
| Institution Type | AI Application | Outcome / Transformation |
| K-12 / College (Bolton) | Video-creation via AI avatars (Synthesia) | Increased digital lesson output, scalability |
| University (Loyola) | AI student-assistant chatbot (LUie) | 24/7 support, higher satisfaction, cost-saving |
| Online / Hybrid (UniDistance Suisse) | AI-tutor with micro-learning & adaptive pathways | 15 percentile point improvement in grades |
| Adaptive-Learning Provider (Knewton) | ML-based adaptive modules for test prep | 62% higher test scores vs control |
Opportunities, Challenges, Ethics & Policy
Opportunities
- Scalability: With AI, institutions can serve larger numbers of learners across geographies, special needs, and remote settings.
- Personalisation: AI enables the move away from “one-size-fits-all” instruction to individualised pathways, boosting engagement and outcomes.
- Efficiency & Productivity: Automating grading, content generation, and administrative workflows frees teachers and staff to focus on higher-value work.
- Data-Driven Improvement: With learning analytics, institutions get rich feedback loops and can continuously refine curricula, instruction, and support.
- Inclusivity: AI tools can assist learners with disabilities, language barriers, and underserved contexts, promoting educational equity.
Challenges
- Data Privacy & Security: Student data is sensitive; institutions must ensure compliance, secure data storage, and transparent use of AI.
- Bias & Fairness: AI models trained on limited or skewed data may perpetuate bias, particularly problematic in education.
- Teacher Training & Adoption: Effective use of AI requires teacher literacy in AI, pedagogy, and change management.
- Technology Infrastructure: Many institutions (especially in developing contexts) lack the bandwidth, devices, and connectivity for AI-powered edtech.
- Ethical Use & Academic Integrity: Tools like generative AI (e.g., ChatGPT) raise questions around cheating, over-reliance, and skill erosion.
- Regulatory & Policy Frameworks: Countries and institutions must develop responsible AI frameworks, teacher policies, and oversight protocols.
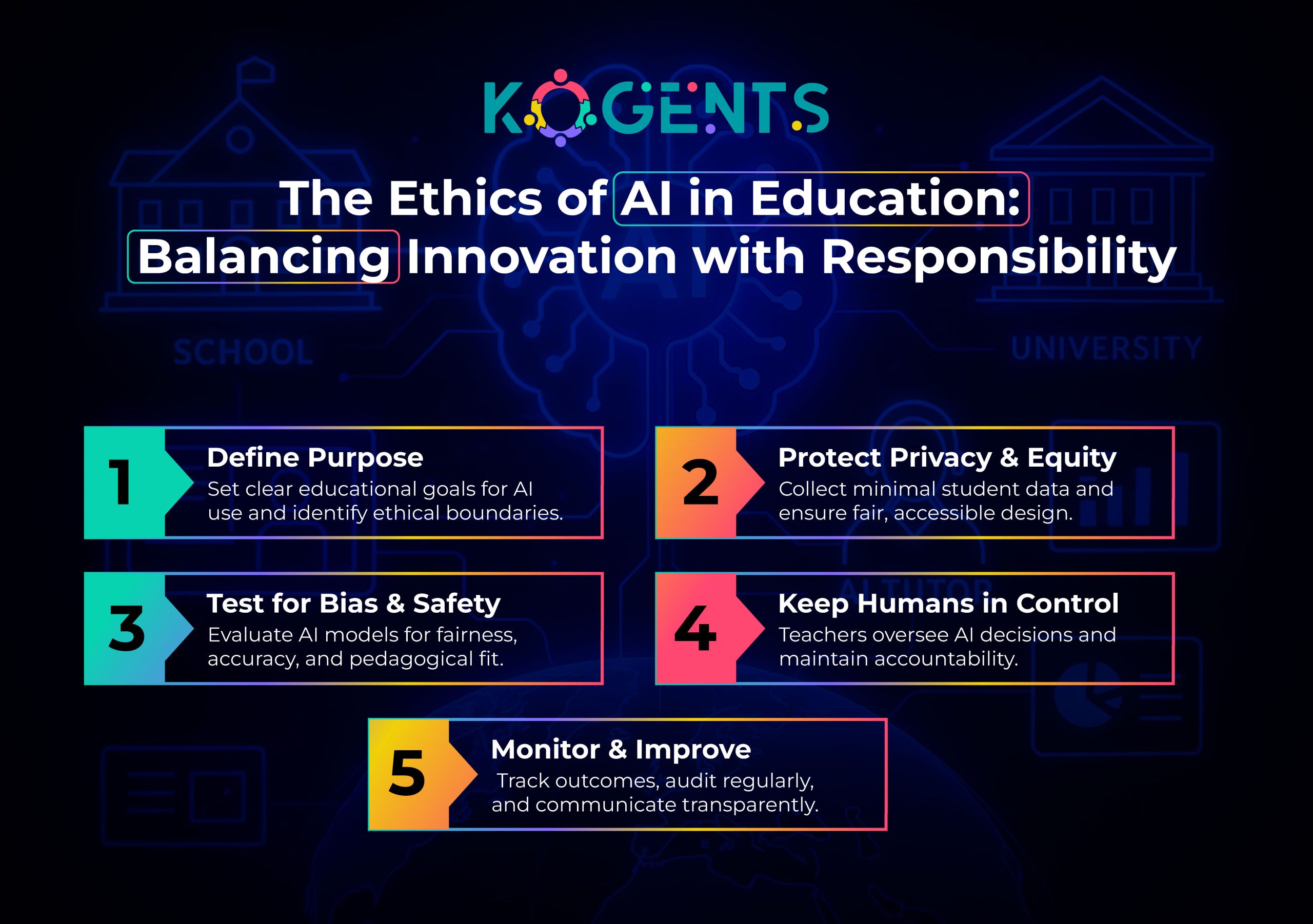
Ethics & Policy Considerations
Institutions must adopt guidelines for ethical AI in education to ensure transparency of algorithms, user consent, auditability of models, and mitigation of unintended biases.
Also important: aligning AI-adoption with pedagogical goals (not merely tech for tech’s sake). Governance must include student voice, educator voice, and oversight.
Conclusion
AI in education examples have been replacing one-size-fits-all teaching with personalised, data-driven learning.
Institutions adopting AI teaching tools, machine learning, and intelligent tutoring systems lead globally.
Adaptive learning and learning analytics empower teachers and elevate student outcomes.
AI frees educators to teach, while data refines every learner’s journey. From K–12 to universities, AI-driven personalisation transforms institutions into global leaders.
Ethical, measurable, and future-ready, that’s the new standard.
The payoff: better outcomes, stronger reputations, and smarter learning.
Partner with Kogents AI, where pedagogy meets intelligent technology.
FAQs
What are examples of AI in education that schools can adopt today?
Examples include adaptive learning platforms that tailor content to each student; AI-chatbots for 24/7 student support; automated grading tools; analytics dashboards for monitoring engagement; AI-driven content creation (videos/quizzes) and intelligent tutoring systems.
How is AI changing classroom learning in K-12 settings?
AI is enabling personalised pace (students move ahead when ready, get remediation when needed), automating administrative tasks so teachers can spend more time interacting with students, supporting students with special needs, and enhancing engagement through smart content, gamification, and smart-classroom sensors.
What are the benefits of AI for students and teachers?
For students: more personalised learning, better feedback, more engagement, ability to learn anytime/anywhere. For teachers: reduced workload, data-driven insights into student progress, ability to focus on pedagogy rather than routine tasks, improved outcomes, and job satisfaction.
How does AI support personalised learning?
By analysing learner data (responses, pace, mistakes, time spent) using machine learning models, AI systems create custom pathways — adjusting content difficulty, recommending resources, and providing targeted feedback — enabling each student to progress at their optimal pace.
How are schools using AI for assessment and grading?
AI can automate objective assessments (quizzes, multiple choice), analyze open responses for patterns (via NLP), flag plagiarism, and give quicker feedback. It also supports formative assessments via micro-questions targeted to learner gaps.
What is the impact of AI in higher education and research?
Higher education institutions are using AI to personalise course materials, provide intelligent tutoring at scale, optimise student services (admissions, support), use analytics to identify attrition risk, and generate content. This helps them become global leaders in reach, reputation, and outcomes.
What are the top AI tools for teachers and students today?
Tools include adaptive learning platforms (e.g., Knewton), AI chatbots (e.g., Oracle Digital Assistant implementations), content-creation tools (e.g., Synthesia), intelligent tutoring systems, and analytics dashboards. Selection depends on institutional context, curriculum, budget, and data maturity.
What are the pros and cons of AI in education?
Pros: personalised learning, efficiency, scalability, better data for decisions, and increased access. Cons: data privacy risks, bias in algorithms, over-reliance on tech, teacher training required, cost of infrastructure, ethical issues around student data, and academic integrity.

Kogents AI builds intelligent agents for healthcare, education, and enterprises, delivering secure, scalable solutions that streamline workflows and boost efficiency.