How Revenue Cycle Automation With AI Cuts Claim Denial Rates and Boosts Margins
Summary:
Against that backdrop, automated revenue cycle management has emerged as a powerful lever to transform financial operations since healthcare providers and payers alike face relentless pressure, be it rising costs, shrinking reimbursements, regulatory complexity, and growing administrative overhead.
One of the most tangible and immediate benefits of automation in the revenue cycle is reducing claim denial rates, those costly rejections, appeals, and rework loops that drain cash flow, morale, and margins.
By applying intelligent revenue cycle automation or AI-driven revenue cycle automation across key subprocesses, healthcare organizations can cut denials, accelerate reimbursements, and unlock margin expansion.
In this comprehensive guide, we explore how and why revenue cycle automation with AI works, present best practices, and offer practical pro tips so your organization can adopt automation with impact.
Key Takeaways
- Revenue cycle automation (and its variants: RCM automation, healthcare revenue cycle automation, automated revenue cycle management) uses AI, RPA, rule engines, and predictive analytics to streamline revenue workflows.
- By catching errors, enforcing payer rules, automating appeals, and performing root-cause analytics, it can dramatically reduce claim denials.
- Automation not only shrinks denials but also trims labor costs, shortens Days in A/R, boosts first-pass acceptance rates, and recovers lost revenue that would otherwise leak.
- To be effective, deployment needs careful planning: integration with EHR/billing systems, change management, exception handling, continuous monitoring, and feedback loops.
What Is Revenue Cycle Automation?
Before diving deep, let’s clarify what we mean by revenue cycle automation and related terms:
- Revenue cycle automation: automating tasks across the revenue cycle (from patient intake through payment posting).
- Revenue cycle management automation: the same concept, emphasizing management plus automation.
- RCM automation: shorthand/acronym usage.
- Automated revenue cycle management: phrase emphasizing automation as the adjective.
- Healthcare revenue cycle automation/revenue automation for healthcare: domain-specific phrasing.
- Revenue cycle workflow automation: focusing on workflow orchestration.
- Automated billing and claims processing: emphasizes claims and billing tasks.
- End-to-end revenue cycle automation: covers the full spectrum of tasks.
- Intelligent revenue cycle automation / AI-driven revenue cycle automation underscores the role of AI, ML, and adaptive logic.
- Robotic process automation for RCM, revenue cycle process automation: variant phrasings emphasizing RPA or process orientation.
- Revenue leak prevention automation, revenue capture automation: emphasizes prevention of lost revenue.
- Claim denial automation, automated eligibility verification / prior authorization/coding / AR automation / automated payment posting: module-level variants.
At its core, revenue cycle automation combines RPA (robotic process automation) for structured, rule-based tasks with artificial intelligence/machine learning / NLP to handle more complex or evolving tasks.
Over time, the system can evolve via feedback loops informed by outcomes and denial analytics, becoming more adaptive.
When fully implemented, end-to-end revenue cycle automation can process much of the cycle with minimal manual intervention, with humans focusing only on exceptions or high-level oversight.

Why Claim Denials Are a Financial Drain?
The Denial Burden
- Claim denials, i.e., when a payer rejects or refuses payment, are among the biggest adversaries of healthy cash flow.
- Denials create rework, appeals, delays, and often permanent write-offs.
According to the American Hospital Association, U.S. hospitals cumulatively hold billions in delayed or unpaid claims over six months out.
Common root causes include:revenue cycle automation
- Missing or inaccurate data (e.g., AI patient scheduling, demographics, subscriber information)
- Lack of or failed prior authorization
- Coding or documentation errors
- Payer rule changes or noncompliance
Impact on Margins
Denials hit margins via multiple levers:
- Slower reimbursement: Denied claims delay cash flow, pushing out Days in A/R (accounts receivable).
- Administrative cost: Each denial takes staff time to investigate, correct, appeal, and resubmit — sometimes costing $10–$50+ per claim depending on complexity.
- Write-offs: Some claims never get resolved and must be written off, directly decreasing revenue.
- Revenue leakage: Repetitive, preventable denials represent money slipping through process gaps.
- Forecasting volatility: High unpredictability in collections undermines budgeting, reserve buffers, and financial planning.
How AI & Automation Cut Denials (Stage-by-Stage)
Here’s how intelligent revenue cycle automation and AI agents for healthcare automation can intervene at each major revenue cycle stage to reduce denials and improve outcomes:
Eligibility & Patient Registration / Intake
Problems encountered: Mistakes in insurance details, demographic mismatches, lapsed coverage, missing subscriber/dependent information, and coordination-of-benefits gaps.
Automation solutions:
- Automated eligibility verification bots that query payer systems in real time to confirm coverage, check benefit details, and flag mismatches early.
- Registration QA / validation tools that cross-check data fields (name, birthdate, insurer ID) before claims submission.
- Workflow prompt alerts to registration staff to correct errors immediately.
Mini Case Story: UT Medical Center
UT Medical Center partnered with Experian Health to deploy Registration QA at intake. This system flagged registration errors before claims generation, catching inaccuracies and missing data.
Prior Authorization
Problems encountered: Procedures requiring preauthorization that were not obtained, missing supporting documentation, payer rejections, delays in approval, and manual entry mistakes.
Automation solutions:
- Rule-based logic engines determine which procedures require prior authorization based on payer, procedure, diagnosis, and historical data.
- Automation bots assemble required documents, submit authorization requests to payer portals, monitor status, send reminders, and auto-escalate delays.
- Denial prediction models detect high-risk authorizations and trigger preventive intervention (e.g., add documentation or escalate).
- Automated appeals for denied authorizations, constructing responses based on templates, and supporting evidence.
Coding, Documentation & Charge Capture
Problems encountered: Incorrect or missing diagnosis/procedure codes (ICD, CPT, HCPCS), missing modifiers, inconsistent documentation, undercoding, or unbilled services.
Automation solutions:
- AI / NLP coding assistants that parse clinical notes, identify diagnoses and procedures, and recommend appropriate codes and modifiers.
- Real-time coding validation: as charges are entered, the system checks for risk, flags missing documentation, or inconsistent combinations.
- Automated charge capture: bots pull charges from clinical systems or device logs to ensure no service goes unbilled.
- Coding edit rules that enforce payer-specific code rules and flag invalid combinations.
Claims Scrubbing & Submission
Problems encountered: Payer rule violations, missing attachments, duplicate claims, invalid payer identifiers, format errors, and business rule mismatches.
Automation solutions:
- Advanced claims scrubbing engines that run multilayered rule checks before submission, validating format, payer rules, attachments, and integrity.
- Dynamic rule updates: systems that auto-adjust to payer updates and new rules.
- Pre-submission denial prediction models: flag claims with high denial risk and route them for manual review or correction.
- Batch submission bots: handle claim submission to clearinghouses or payer portals, track acknowledgments, catch rejections early, and requeue for correction.
Reminder: When claims are “clean,” denial volumes drop sharply and first-pass acceptance improves.
Mini Case Story: St. Luke’s Health System
St. Luke’s Health implemented Enhanced Claim Status automation (via Experian) to automate submission, status tracking, and error resolution.
They reduced their denial rate dramatically — from ~27% to 6.5%, resulting in a 76% decline in denials.
That kind of leap underscores the power of workflow automation combined with real-time status tracking.
Denial Management, Appeals & Root-Cause Analytics
Problems encountered: Manual classification of denials, missed appeals, lack of priority routing, no feedback loops to fix root causes, document gathering inefficiencies, and long resolution times.
Automation solutions:
- Denial detection and classification bots: automatically categorize denials by code, payer, department, severity, likelihood of overturn, and route them to appropriate queues.
- Automated appeals generation: using templates and logic, bots draft appeal letters, gather supporting documentation, fill out payer forms, and file appeals.
- Prioritization workflows: the system emphasizes high-dollar or likely success cases first.
- Root-cause analytics: AI tracks denial trends by payer, code, department, clinician, and surfaces common denial drivers for process improvement.
- Auto-posting of appeal outcomes: once appeals succeed, bots update the billing systems, post payments, and update dashboards.
Mini Case Story: Guidehouse + Health System
Guidehouse worked with a major remote health monitoring system to deploy intelligent automation across 13 business functions, including insurance eligibility and denial resolution.
Their analysis found over $44 million in denied accounts needing rework. By optimizing core systems and deploying RPA / conversational AI, they impacted millions in saved or recovered revenue and recaptured over 2,000 hours of employee time for higher-value work.
Payment Posting & Reconciliation
Problems encountered: Manual posting errors, unmatched payments, failure to capture remittance adjustments, and delays in reconciling payer responses.
Automation solutions:
- Automated payment posting bots: parse Electronic Remittance Advice (ERA) files, match payments, apply adjustments, and post to accounts automatically.
- Exception-handling logic: flags mismatches or ambiguous cases to staff for manual review.
- Reconciliation workflows: bots match payer responses, generate variance reports, and clean up inconsistencies.
Before vs After — Key Metrics Impact
| Metric | Before Automation | After Automation / Target | Improvement / Impact |
| Claim Denial Rate | 8–12% | 3–5% | ~40–70% reduction |
| First-Pass Acceptance | 70–80% | 90–95% | +10–20 pts |
| Days in A/R | 60–90 days | 30–45 days | ~30–50% reduction |
| Cost per Denial Work | $15–40 | $5–15 | ~60% cost saving |
| Appeal Overturn Rate | 20–30% | 60–90% | +2–3× |
| Cash Flow Recovery / Year | $0 (baseline) | $2–10M+ (depending on size) | Multi-million gain |
| Labor / FTE Hours Saved | Many hours of manual rework | Reallocated to high-value tasks | Efficiency gain |
| Write-offs / Bad debt | High level | Lowered by 30–60% | Margin boost |
Pro Tips & Best Practices for Smooth Implementation
- Phase your deployment
Begin with high-impact modules (eligibility, scrubbing, denial automation), prove value, then scale outward. - Strong integration architecture
Ensure seamless connectivity with EHR, billing, clearinghouse systems, payer portals, and document systems. Use APIs, ETL layers, or middleware as needed. - Process discovery & mapping
Use process mining or advisor tools to document current state flows, identify bottlenecks, and pinpoint automation opportunities. - Establish baseline metrics before automation: denial rate by payer, first-pass acceptance, days in A/R, appeal overturns, cost per denial, write-offs.
- Feedback loops & continuous learning
Feed denial results and appeal outcomes back into the model so the automation “learns” and evolves. - Human-in-the-loop & exception frameworks
Design workflows so that ambiguous or unusual cases escalate to staff, rather than forcing rigid automation. - Staff engagement & change management
Involve revenue cycle staff early, train them, show quick wins, and reframe automation as augmenting rather than replacing work. - Governance, audit, compliance
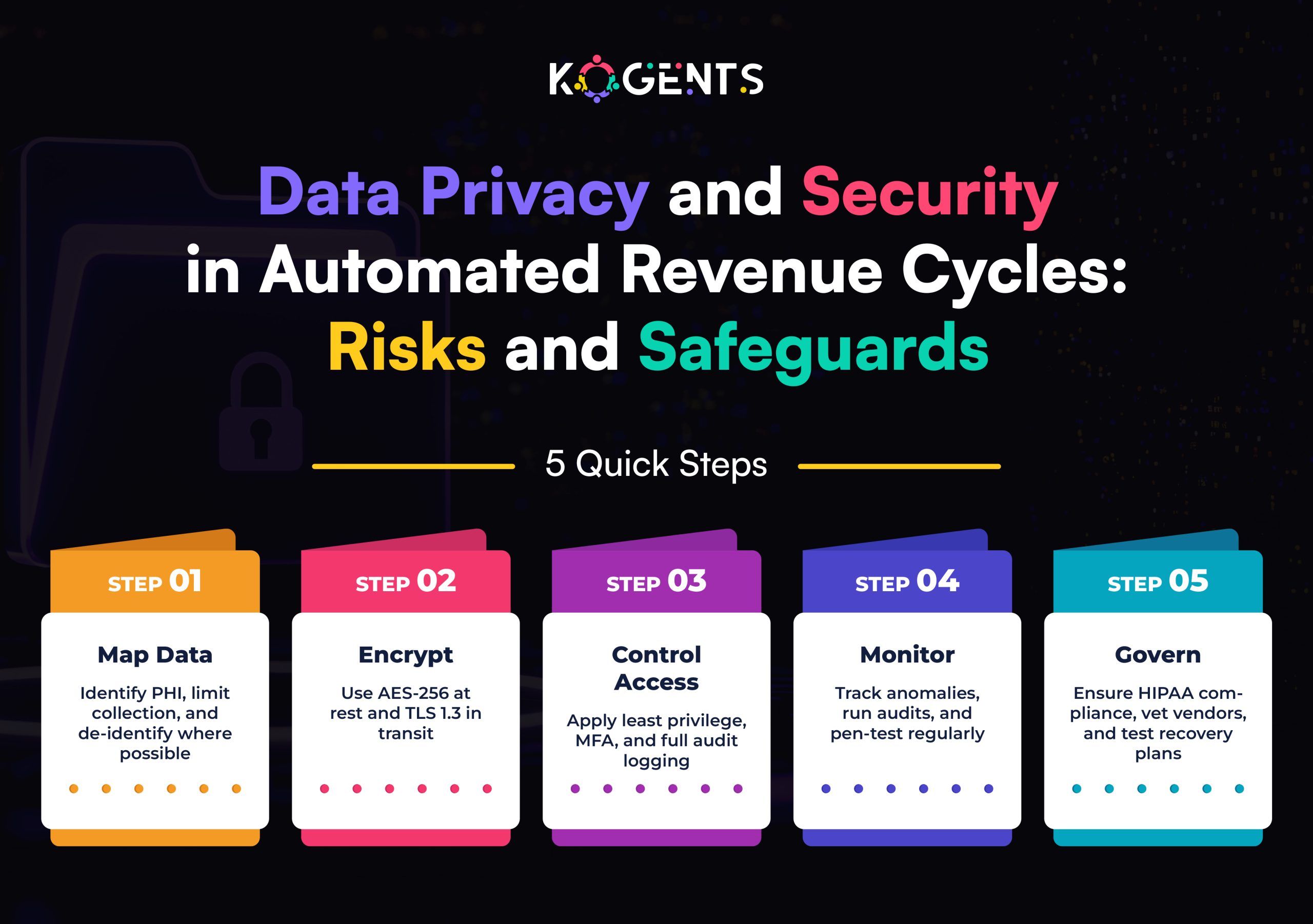
Enforce logging, version control, audit trails, HIPAA compliance, and data security. Use vendors with SOC2 / HITRUST credentials. - Pilot in shadow mode
Run bots in parallel with human work for a time to validate accuracy and refine logic before fully flipping control. - Vendor evaluation & fit
Prioritize vendors with deep healthcare RCM experience, AI/NLP capabilities, and strong references. Seek KLAS-ranked or HFMA-recognized partners.
Conclusion
In an era of tightening reimbursements, complexity, and margin pressure, revenue cycle automation enhanced by AI is rapidly becoming indispensable rather than optional.
By intervening at every stage, from eligibility verification to appeals and payment posting, automation can severely compress claim denial rates, accelerate cash inflows, reduce administrative burden, and protect margins.
If your organization is exploring automated billing and claims processing, intelligent revenue cycle automation, or building toward end-to-end revenue cycle workflow automation, this is your moment to pair up with Kogents.ai. Give us a call at +1 (267) 248-9454 or drop an email at info@kogents.ai.
FAQs
What is revenue cycle automation, and how does it differ from RCM?
Revenue cycle automation focuses on using software, bots, AI, and workflows to automate tasks within the revenue cycle. RCM (revenue cycle management) is the end-to-end discipline of managing financial operations. When automation is overlaid, you get revenue cycle management automation, automated revenue cycle management, or AI-driven revenue cycle automation.
How exactly does automation reduce claim denials?
Automation catches errors early (eligibility, registration), applies payer rules in coding and scrubbing, predicts high-risk claims for preemptive correction, routes denials intelligently for appeal, and closes feedback loops to prevent repeat denials.
What technologies underpin intelligent revenue cycle automation?
Key building blocks include RPA (robotic process automation), AI/machine learning, NLP / natural language processing, rule engines, workflow orchestration, and predictive analytics. The synergy of these enables more context-aware and adaptive behaviors.
How do RPA and AI differ in this context?
RPA handles structured, repetitive, rule-based tasks (e.g., copying, populating forms). AI adds decision-making, prediction, natural-language understanding, anomaly detection, and adaptivity. The most powerful architectures combine both.
Will automation replace revenue cycle staff?
No, the goal is to augment staff, freeing them from repetitive work so they can focus on exceptions, strategy, analytics, and oversight. Many teams reassign FTEs to higher-value tasks.
FAQs
Revenue cycle automation focuses on using software, bots, AI, and workflows to automate tasks within the revenue cycle. RCM (revenue cycle management) is the end-to-end discipline of managing financial operations. When automation is overlaid, you get revenue cycle management automation, automated revenue cycle management, or AI-driven revenue cycle automation.
Automation catches errors early (eligibility, registration), applies payer rules in coding and scrubbing, predicts high-risk claims for preemptive correction, routes denials intelligently for appeal, and closes feedback loops to prevent repeat denials.
Key building blocks include RPA (robotic process automation), AI/machine learning, NLP / natural language processing, rule engines, workflow orchestration, and predictive analytics. The synergy of these enables more context-aware and adaptive behaviors.
RPA handles structured, repetitive, rule-based tasks (e.g., copying, populating forms). AI adds decision-making, prediction, natural-language understanding, anomaly detection, and adaptivity. The most powerful architectures combine both.
No, the goal is to augment staff, freeing them from repetitive work so they can focus on exceptions, strategy, analytics, and oversight. Many teams reassign FTEs to higher-value tasks.

Kogents AI builds intelligent agents for healthcare, education, and enterprises, delivering secure, scalable solutions that streamline workflows and boost efficiency.