Understanding What Is Workflow Automation in the Era of AI Agents and Predictive Logic
Summary:
Imagine a workplace where the mundane tasks, the repeated clicks, countless approvals, and manual hand-offs are no longer bottlenecks but instead quietly hum in the background.
Instead of chasing spreadsheets and chasing signatures, your team strategizes, innovates, and moves fast.
That is the vision behind what is workflow automation, but not just in its classic sense: this is automation infused with the power of AI agents, predictive logic, and orchestration at scale.
In this new era, the definition of automation has shifted. It’s not simply “automate a task” but “automate a workflow intelligently, dynamically, adaptively.” That means your system anticipates the next step, takes context into account, uses data to predict outcomes, and uses agentic AI to execute or recommend.
The result? A leap from rule-based task automation into the realm of intelligent workflow orchestration.
This blog is your quick guide to understanding workflow automation, its meaning, evolution with AI, and real-world impact on modern business efficiency.
Key Takeaways
- Workflow automation is no longer just rule-based: it’s integrating AI agents, predictive analytics, and workflow orchestration to adapt and act.
- The difference between business process automation (BPA) and workflow automation matters; understanding that distinction unlocks a better strategy.
- The era of AI agents (often referred to as AgentOps) is reshaping how workflows are built, managed, and governed.
- Selecting the right tools, aligning with business objectives, tracking key metrics (e.g., cost-savings, productivity, error-reduction), and orchestrating human + machine collaboration are critical for success.
Decode: What Is Workflow Automation First!
At its core, workflow automation refers to the process of using technology to streamline, manage, and execute a sequence of tasks or activities without requiring continuous human intervention.
In simple terms, you map out a workflow (for example: “employee onboarding” or “invoice approval”) and then implement a system that automates the movement of tasks, triggers events, routes approvals, integrates data, and monitors statuses so that the process becomes faster, less error-prone, and more visible.
Evolution: From Rule-Based Automation to AI-Driven Workflow Orchestration
In the early days, workflow automation tools/software were primarily rule-based: “If this happens, then do that” (IFTTT).
They were good at automating manual hand-offs, simple data routing, email approvals, and triggering notifications. In other words: static flows and predefined rules.
But as digital transformation accelerated, businesses realized these static flows lacked adaptability, context-awareness, and intelligence.
That’s where the next generation entered with predictive logic, machine learning, intelligent process automation (IPA), and now AI agents.
Key milestones in the evolution:
- No-code / low-code automation platforms: democratizing workflow creation for business users.
- Robotic Process Automation (RPA): bots that replicate human interactions in systems (data entry, file uploads, etc).
- AI-powered automation: systems that use machine learning and natural language processing (NLP) to handle unstructured data, exceptions, and decisions.
- Agentic automation / AgentOps: orchestrating autonomous AI agents that coordinate workflows across systems, make decisions, and self-optimize.
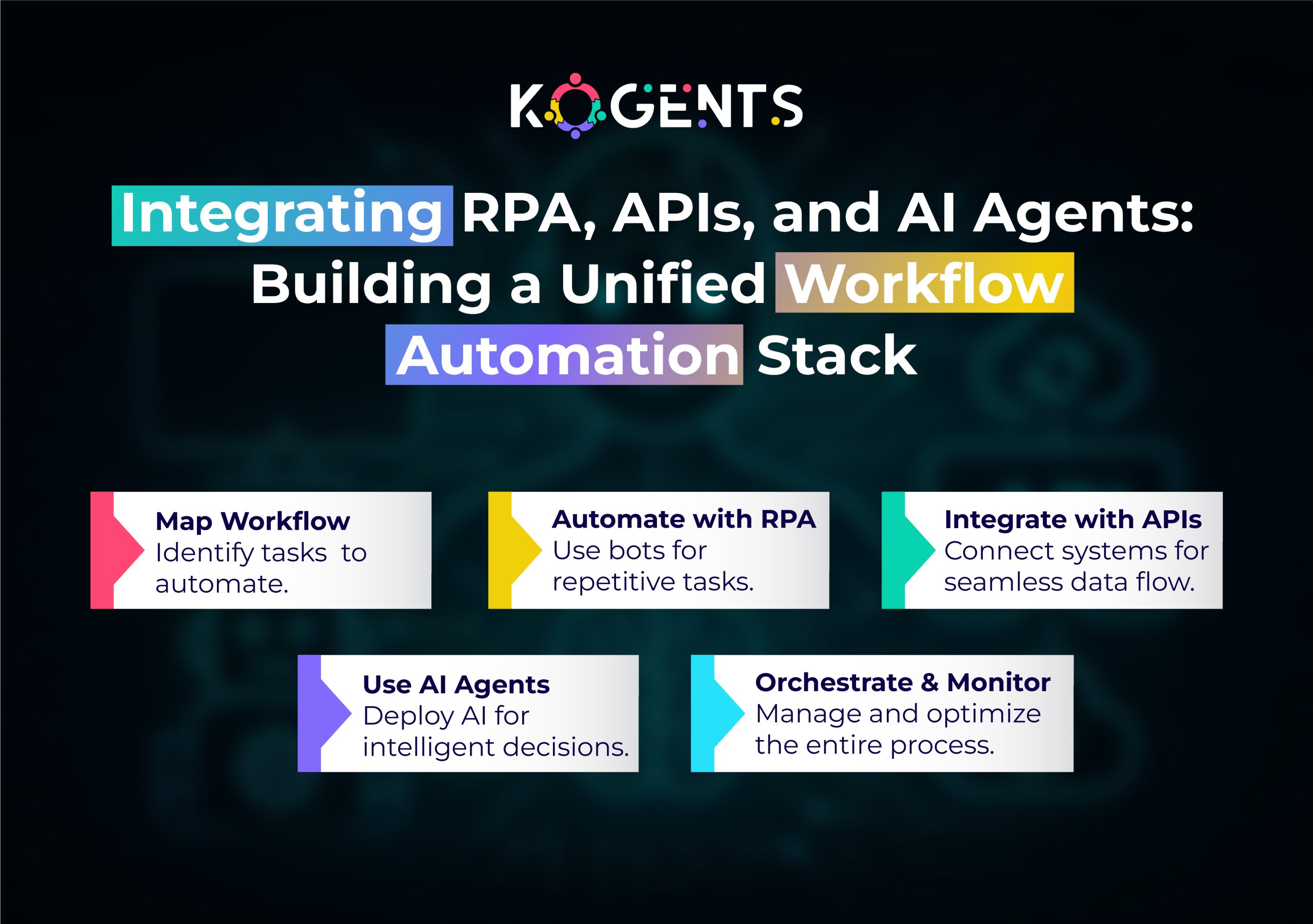
How Workflow Automation Works – Mechanisms, Components, Architecture?
Understanding how workflow automation works is critical for effective design and implementation.
Components of a Workflow Automation System
- Trigger/Event: An action that initiates the workflow (e.g., new invoice submitted, form completed).
- Tasks/Steps: Defined activities that need to happen (assign review, send approval, update system).
- Rules & Conditions: Logic that determines path, branching, and exceptions.
- Integrations/APIs: Connectors to other systems (CRM, ERP, SaaS apps, databases).
- Workflow Engine/Orchestrator: The core that tracks state, routes tasks, and triggers next steps.
- Automation Bots/Agents: Execution layer (could be rule-based bots or AI agents).
- Monitoring & Analytics: Dashboards & metrics to track performance, bottlenecks, and KPIs.
- Governance & Compliance: Ensuring policies, data security, and audit trails.
Differences: Workflow Automation vs Business Process Automation (BPA)
| Feature | Workflow Automation | Business Process Automation (BPA) |
| Scope | Focuses on automating a specific sequence of tasks (workflows) within a process. | Broader: automates entire business processes, including complex cross-functional flows. |
| Granularity | Task-level or subprocess-level. | End-to-end process level (may include multiple workflows, decisions, data flows). |
| Complexity | Relatively contained, often rule-based. | Higher complexity may involve decision logic, analytics, optimization, and human-in-the-loop. |
| Tools | Workflow engines, BPM, and no-code platforms. | BPA includes BPM suites, RPA, decision engines, and AI. |
| Typical Use | Approval workflows, data routing, and routine onboarding. | Loan origination, procure-to-pay, customer lifecycle management. |
The Role of AI Agents & Predictive Logic in Workflow Automation
This is where the era of automation shifts into high gear.
What Are AI Agents?
AI agents, more specifically workflow automation AI agents, are software entities that can perceive, reason, act, and learn within an environment.
They go beyond rule-based bots, using predictive logic, machine learning, natural language processing (NLP), and can coordinate across systems.
Example: an AI agent may: extract data from an email, classify it, decide which workflow to trigger, perform the action, escalate if exceptions occur, and learn from feedback.
Why Predictive Logic Matters?
It uses historical data, patterns, and statistical models to anticipate what the next step should be.
In the context of workflow automation:
- Predict which invoices are likely to get delayed and trigger alerts.
- Forecast which requests require manual review vs which can be auto-approved.
- Route tasks to the right person based on capacity and skill.
How does this change workflow Automation?
- From reactive to proactive: not only automating tasks after the fact, but also anticipating tasks and acting ahead of time.
- From static flows to adaptive flows: workflows that adapt to context, data, and exceptions.
- From human-in-the-loop to human-on-the-loop: humans supervise and intervene when needed; AI agents handle standard flow.
- From segmented automation to orchestration: agent layers coordinate tasks across multiple systems, data sources, and silos.
Unravel the Benefits of Automating Workflows!
What are the tangible benefits when you implement workflow automation? Let’s list some major ones.
Efficiency & Time-Savings
- Manual, repetitive tasks (forms, approvals, routing, data entry) take significant time.
- Automating those frees employees for higher-value work.
Example: 52% of business leaders believe that 10-30% of their daily tasks can be automated.
- Productivity improvement: a report shows automation improved jobs for 90% of knowledge workers and productivity for 66%.
Accuracy & Error Reduction
- Human errors, data entry mistakes, missed approvals, incorrect routing, carry cost, and risk. Automation minimizes those.
According to stats, automation reduces capture process errors by 37% and boosts data accuracy by 88%.
Cost-Savings & ROI
- Hard cost reduction (fewer manual hours, faster turnarounds, fewer errors) plus soft benefits (better employee satisfaction, fewer bottlenecks) yield strong ROI.
Scalability & Agility
- Workflows scale as the business grows without a proportionate increase in headcount or manual effort.
- Predictive logic and AI agents mean you can adapt to changing business conditions, rather than rebuild flows from scratch.
Visibility & Process Improvement
- Automation brings real-time monitoring, dashboards, and workflow analytics, so you see bottlenecks, cycle times, and inefficiencies.
- Businesses can then continuously improve processes.
Improved Employee Experience & Strategic Focus
- By removing low-value tasks, employees can focus on more strategic, creative, or value-added work.
- This leads to higher morale, better retention, and ultimately innovation.
Highlight: When you ask about the benefits of business process workflow automation, these are the drivers that gather support at executive levels.
Workflow Automation Use Cases & Examples in Business/Enterprise
Let’s walk through concrete use cases where workflow automation examples are crucial.
In a Gartner survey, 80% of executives believe automation can be applied to any business decision.
Use Case: Invoice Approval & Accounts Payable
A very common workflow in finance: invoice submission → review → approval → payment. Workflow automation ensures routing, reminders, validating invoice data, and logging.
With AI agents:
- Automatic extraction of invoice data (IDP)
- Predictive logic flags high-risk invoices
- Agent routes for manual review only when an exception occurs, and integrates with ERP.
Use Case: Customer Support & Service Requests
Workflow automation is applied to ticket routing, approvals, and escalations.
With AI agents and predictive logic: the agent triages incoming tickets (via NLP), routes to the correct queue, escalates if SLA breaches, and automatically triggers feedback workflows.
Use Case: Supply Chain / Order Management
Orders arrive from multiple channels, inventory needs to be update, and vendors notified.
Workflow automation handles the tasks; AI agents predict inventory shortages, suggest alternative sourcing, and trigger order adjustments.
In manufacturing, this means fewer stock-outs, faster fulfillment.
Use Case: Marketing & Campaign Management
Workflows may include campaign planning, asset approvals, email scheduling, and performance tracking.
With AI agents:
- Predictive logic suggests optimal send times
- automates copy generation (via generative AI)
- routes tasks to appropriate team members
- optimizes campaign flow.
Case Studies – Real-World Applications and Outcomes
Here are three credible, non-repetitive case studies aligned with our topic.
Case Study: Corporate Expense Processing – Generative AI + Automation Agent
A major Korean enterprise implemented an end-to-end process automation system that combined generative AI, Intelligent Document Processing (IDP), and an Automation Agent to handle receipt-based expense tasks.
The solution: OCR/IDP for receipts, classifier based on policy, intelligent exception handling via generative AI, human-in-the-loop decisions, and continuous learning.
Outcomes: over 80% reduction in processing time, decreased error rates, improved compliance.
Bring It All Together With Kogents!
In an age where every business is striving for operational efficiency, agility, scalability, and a competitive edge, understanding “what is workflow automation” takes on a deeper meaning.
With the rise of AI agents, predictive logic, and orchestration platforms, workflow automation has entered a new frontier.
The business benefits are clear: fast cycle times, fewer errors, lower cost per transaction, and more time for employees to focus on strategic work.
So, where does kogents.ai come into the picture? Here, we empower businesses to harness advanced workflow automation by integrating AI agents, predictive logic, intelligent orchestration, and scale smart automation solutions.
FAQs
What is workflow automation in simple terms?
At its simplest, workflow automation means using software to move tasks, information, and approvals automatically through a sequence of steps (a workflow) instead of doing them manually. It speeds things up, reduces errors, and makes processes more consistent.
How does workflow automation work?
It works by defining triggers (e.g., form submitted), mapping the steps/tasks, setting decision logic (conditions, branches), integrating systems (CRM, ERP, APIs), deploying bots/agents to execute tasks, and using monitoring & analytics to measure performance. With AI-agents and predictive logic, the system can anticipate next steps, learn from data, and adjust.
What is the difference between workflow automation and business process automation?
While both aim to automate processes, workflow automation typically refers to automating a specific sequence of tasks within a process. Business process automation (BPA) is broader and may encompass complex, cross-departmental, end-to-end processes with decision logic, analytics, cs, and optimization. Workflow automation is often a subset of BPA.
How to automate workflows in small businesses?
For smaller businesses, start by mapping your manual, repetitive tasks (forms, approvals, data routing). Choose a user-friendly, affordable workflow automation tool (e.g., a no-code platform). Automate one workflow at a time, measure results, iterate, and build from there. Prioritise high-impact tasks (time-consuming, error-prone). As you scale, you may integrate predictive logic or AI capabilities.
What are the best practices for workflow automation implementation?
Some best practices: start with process mapping and baseline data; involve stakeholders; prioritise high-impact workflows; define clear KPIs; choose tools with good integration; ensure governance; include exception-handling; train users; monitor performance and iterate; scale gradually; assess ROI.
How is workflow automation changing with AI agents and predictive logic?
Previously, workflow automation was rule-based and static. Now, with AI agents and predictive logic, workflows become adaptive, context-aware, and even proactive. AI agents can extract data from unstructured sources, predict next steps, route tasks intelligently, optimize workflows dynamically, and learn over time. This marks a shift toward orchestration and intelligence, not just automation of tasks.

Kogents AI builds intelligent agents for healthcare, education, and enterprises, delivering secure, scalable solutions that streamline workflows and boost efficiency.